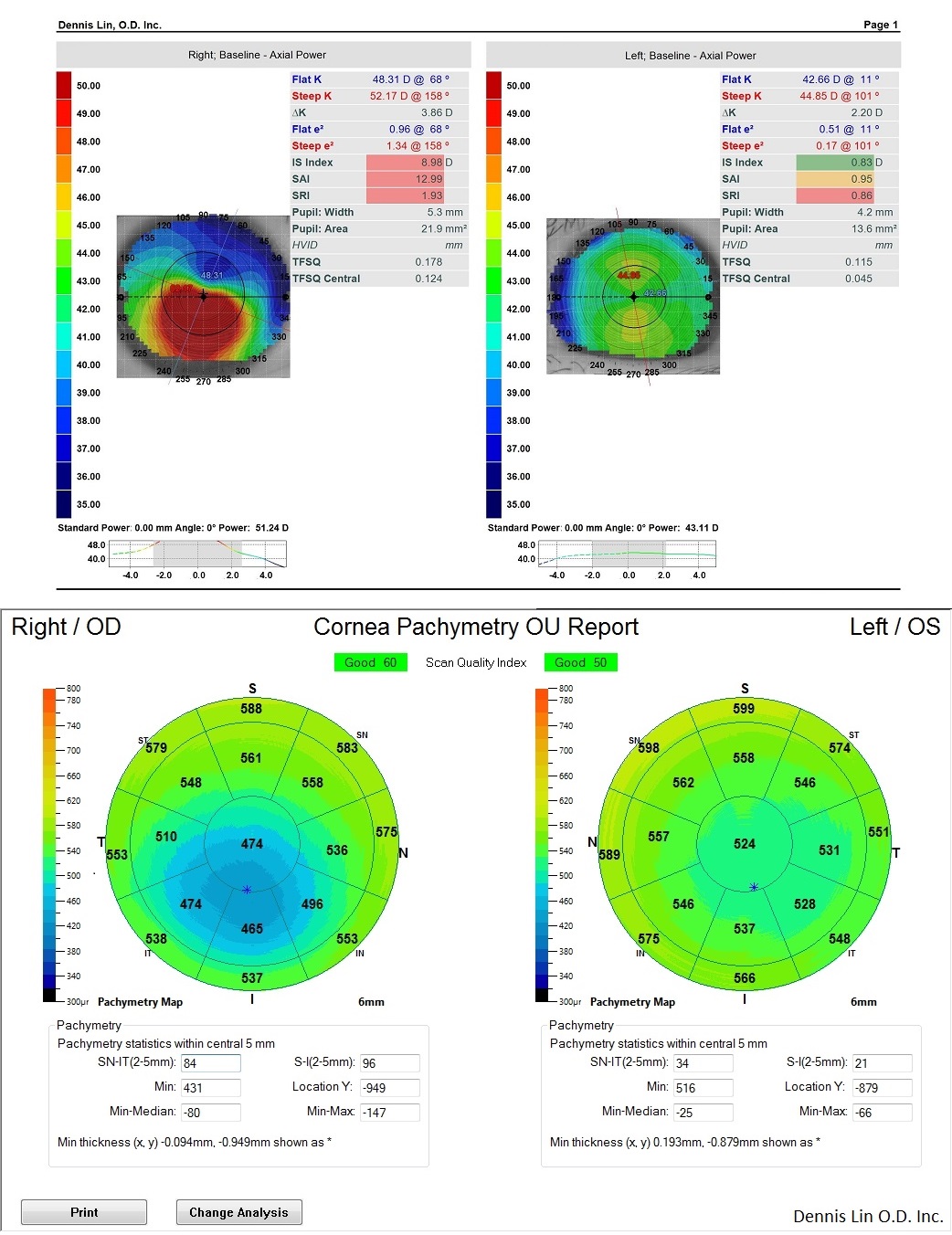
Samples of Topography and Pachymetry data results.
[ CLICK TO VIEW EXAMPLES ]
Corneal topography is recommended to measure the absolute steepest part of the cornea at the height of the cone (More Accurate). If a corneal topographer is not available, use a manual or auto-keratometer (Not as precise).
MILD KERATOCONUS
Steepest corneal curvature of ≤ 48.00D
MODERATE KERATOCONUS
Steepest corneal curvature of 48.00D to 53.00D
ADVANCED KERATOCONUS
Steepest corneal curvature of ≥ 53.00D
The average corneal thickness is “approximately” 555 μm. An Ultrasound pachymeter is helpful but an Optical Coherence Tomographer pachymetry would give more precision.
MILD KERATOCONUS
Lowest corneal thickness of ≥ 500μm
MODERATE KERATOCONUS
Lowest corneal thickness of 300μm – 500μm
ADVANCED KERATOCONUS
Lowest corneal thickness of ≤ 300μm
List of Keratoconus ICD-10 reference codes.
Disclaimer: Please note that we are not billing experts so please use caution. These codes are not meant to help and must be verified.
CONTACT LENS FITTING
CONTACT LENS MATERIAL
OTHER CODES
Steep Corneas: Central K > 48.0 D
Thin central cornea : Pachymetry < 470 um
Inferior and Superior K Topographical Difference > 1.4 D
Asymmetry Between the Right and Left Eye Curvature ( > 1.9 D difference central Ks)
Large Difference Between Thinnest and Central Points ( >30 um)
Difference of > 23 um in Central Corneal Thickness between 2 eyes
Irregularity >1.5 D and > 2.0 D at 3.0 and 5.0 mm zones
Posterior elevation >0.050mm Note: Earliest Ectatic changes can only be seen in the posterior cornea
Posterior cornea and elevation maps: Posterior elevation > +10 is suspicious
BCVA uncorrectable to 20/20
Oblique astigmatism
Scissoring reflex on retinoscopy
Oil droplet reflex on Direct Ophthalmoscopy
Munson sign (Inferior Gaze)
Rizutti sign –conical reflection with angled light source on cornea
Vogt’s Striae – Stromal striae
Fleisher Ring – Epithelial iron deposits – Best viewed with Blue Cobalt Light
Central or Inferior Corneal Thinning
Acute Hydrops (Later sign of Keratoconus)
Corneal Stromal Scarring (Resultant of hydrop and later sign of Keratoconus)
Difficult and variable subjective refractions
Autorefractor Readings and Subjective Refractions are vastly different
Patient often unhappy with glasses
More spectacle remakes
Rapidly increasing astigmatism and/or oblique astigmatism
Increased steeping on Keratometry readings from previous visit
Frequent rubbing of eyes
Complaints of Glare and Haloes and Difficulty with Night Driving
Vision was good until sudden worsening in High School – College years
Quickly changing from spherical contacts to toric contacts for astigmatism
Poorly fitting soft contacts